How Much Car Insurance Do I Need?
Get the right amount of auto insurance coverage for your vehicle.
 Maskot/Getty Images
Maskot/Getty Images
Auto insurance is an essential part of owning and driving a car, but deciding how much to get can be challenging. In this article, you’ll learn about different coverage options and how to determine the amount of car insurance to fit your needs and budget.
Why Do I Need Car Insurance?
Some states require car insurance in order to operate a vehicle, so you don’t have to be a reckless driver to be at risk when you get behind the wheel. As long as there are other drivers on the road, there is the possibility of a crash, and with that comes the financial risk of property damage and medical expenses.
And when the cost of a car crash can range from a couple hundred dollars to millions, it’s no laughing matter.
But here’s the good news: Car insurance is designed to help protect drivers from bearing that financial burden alone. How much help you get depends on the types and amount of coverage you choose.

Talk with your AAA Insurance Agent to help find out which type of coverage is best for you and your family.
Learn MoreCommon Types of Car Insurance Coverage
We often talk about car insurance as if it’s one size fits all. But the truth is there are many different types of coverage, each with its own capabilities and limits, and you can combine them to create a policy that fits your specific needs and risk tolerance.
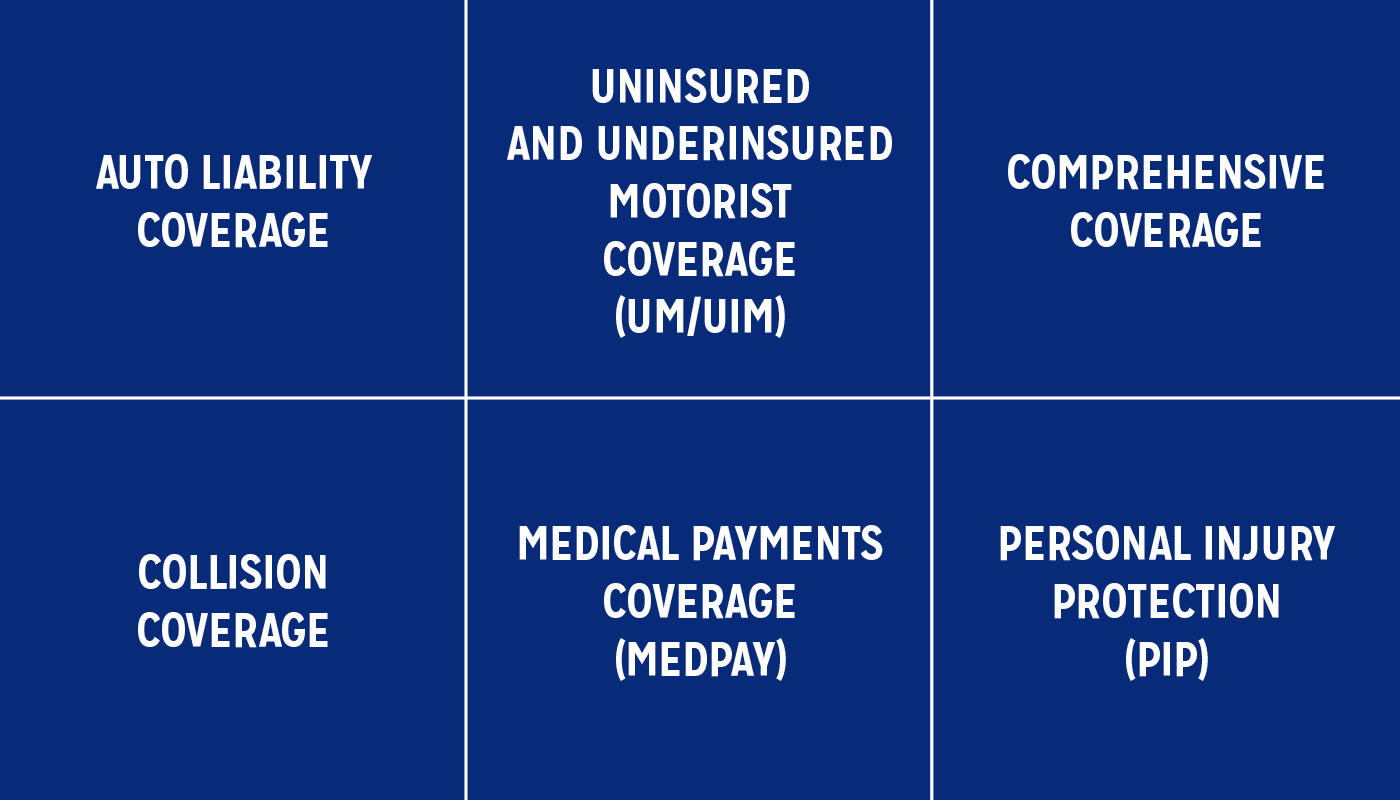
Auto Liability Coverage
If you cause a car crash, you may be held responsible for others’ medical expenses and property repairs. Liability insurance helps shoulder those costs. Most states (and lenders) have minimum coverage requirements for bodily injury liability and property damage, although you may choose to pay for more coverage.
Uninsured and Underinsured Motorist Coverage (UM/UIM)
In a car crash caused by a driver with little or no insurance, uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage can help pay for property damage, as well as medical bills if you or your passengers are injured. It may also be used if you are the victim of a hit-and-run crash.
 iStock
iStock
Comprehensive Coverage
Of course, you don’t have to be driving your car for it to be damaged. Theft and vandalism; weather-related damage from hail, flooding or falling objects; hitting an animal or road debris—all of these can be expensive. Fortunately, that’s where comprehensive coverage may come into play.
Collision Coverage
For vehicle damage from a driving-related incident such as a parking lot fender-bender or an unexpected pothole, you need collision coverage.
 iStock
iStock

Medical Payments Coverage (MedPay)
Where liability coverage only pays for others’ medical expenses in a crash where you’re at fault, medical payments insurance covers medical costs for you and your passengers, regardless of who’s at fault. You’re also covered if you are a passenger in someone else’s car or if you’re injured as a pedestrian.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Personal injury protection, or PIP, coverage is similar to medical payments coverage because it also covers medical expenses for you and your passengers, no matter who’s at fault. However, it can also help pay for lost wages, funeral expenses and more.
How Much Car Insurance Do I Need?
Every state has different requirements for car insurance. Some require only auto liability coverage, while others may also require coverage for uninsured motorists or medical payments. The minimum coverage requirements vary widely by state, ranging from:
- $10,000–$50,000 in bodily injury liability per person
- $20,000–$100,000 in total bodily injury liability per crash
- $5,000–$25,000 in property damage liability per crash
If required in your state, coverage for uninsured/underinsured motorists can range from:
- $20,000–$50,000 bodily injury per person for UM/UIM
- $40,000–$100,000 total bodily injury per crash for UM/UIM
- $5,000–$25,000 in property damage per crash for UM/UIM
Of course, you can carry more coverage than the minimum requirement—in fact, many people do.
If you choose to carry additional insurance coverage such as comprehensive or collision coverage, you’ll have to pay a deductible. That’s the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in to help. The average auto insurance deductible is $500. You may be able to choose a higher or lower deductible if you prefer, but keep in mind that a lower deductible will increase your premium while a higher one will decrease it.
Use These Questions To Help You Decide
The types and amounts of car insurance you carry will also depend on your personal needs, budget and risk tolerance. Here are a few things you may want to consider:
- Are you driving a brand-new car or an older vehicle?
- Do you own your car outright, or are you financing or leasing it?
- Where do you live, drive and park your car?
- Are you the only driver, or do other members of your household drive the car?
- Do you have enough savings to pay for medical expenses and repairs out of pocket if necessary?
- Can you afford a higher deductible?
Full Coverage Auto Insurance
Full coverage isn’t actually a type of insurance coverage. It simply refers to an auto insurance policy that includes auto liability, comprehensive, collision and uninsured motorist coverages. For a full coverage policy, insurance agents typically recommend a 100/300/50 liability policy, meaning:
- $100,000 in bodily injury per person
- $300,000 in total bodily injury per crash
- $50,000 in property damage per crash
With full coverage car insurance, your vehicle is covered for a variety of situations—whether damage is caused by a collision or other incident, regardless of whether you’re at fault or not.
While full coverage is not a requirement in most states, you may find that your lender requires it if you finance or are leasing your vehicle.
 iStock
iStock
Gap Coverage
If your vehicle has been totaled in a crash or other covered incident, your insurance company pays the actual cash value of your vehicle, minus your deductible.
But what if that payment is less than what you owe on your car loan? Without cash on hand, you could be in trouble—unless you have GAP coverage. GAP stands for Guaranteed Asset Protection, and it covers the gap between what you owe and the actual cash value of your car. While not required, this add-on coverage can give you greater peace of mind.
Minimum Liability Coverage
On the other end of the spectrum, minimum liability coverage is just what it sounds like: the bare minimum required by law. While this is usually the cheapest car insurance option, it does leave you exposed to financial risk.
What Happens If I Don’t Have Car Insurance?
Make no mistake—the consequences of driving without auto insurance can be legally and financially devastating: license and registration suspension, fines, reinstatement fees, vehicle impoundment and even jail time, not to mention paying out of pocket for car repairs and medical expenses if you're in a crash. Of course, if you’re not able to pay, you could get sued, and then all your assets could be at risk.
 iStock
iStock
Here are some of the more practical reasons why you need car insurance:
- Help with non-crash damage. Car crashes aren’t the only cause of vehicle damage. Without comprehensive coverage, you pay out of pocket for theft, vandalism, weather-related damage and more.
- Rental reimbursement. Some car repairs take several days or even weeks. If you need to rent a car during that time, you won’t have insurance to reimburse the cost.
- No Pay, No Play laws. Some states have laws that prevent uninsured drivers from receiving financial damages for pain and suffering after a crash, even if another driver was at fault.
Get Protection for the Road Ahead With AAA Car Insurance
With car insurance through AAA, you can find coverage that fits your needs and budget while giving you peace of mind when you hit the road.
This information is being provided for general informational purposes only. The Auto Club Group does not assume any liability in connection with providing this information.
Coverage is subject to all policy terms, conditions, exclusions and limitations. Discounts and savings opportunities subject to eligibility requirements. Subject to underwriting requirements. AAA Insurance is a collection of AAA branded insurance products, services, and programs made available to qualified members. Personal lines insurance is underwritten by [insert applicable underwriting companies for those states that this will be used in] ©2024 The Auto Club Group. All rights reserved.